
Listening devices technology can be either innovative or fundamental and is quickly improving to benefit wearers more than ever in the past.
Listening devices innovation has enhanced a lot over the past couple of years, but at their core, hearing aids have actually always been developed with 4 standard parts: a microphone, a processor, a receiver and a source of power. The microphone gets the noises in your environment and passes it to the processor. The processor improves the signal and provides it to the receiver which provides the magnified signal to the ear canal. The power source, or battery, drives the system.
Listening devices technology can be considered either advanced or basic, based on the elegance of the processor. Even today's fundamental digital hearing aids provide even more advantage than the best hearing aids of previous generations.

New and advanced listening devices technology
As the level of innovation increases, digital hearing aids end up being more automatic and have more functions to assist you interact in difficult listening situations. New technologies translate to greater rate points for hearing aids and higher advantages. The following features are more likely to be used in innovative hearing aids. Note that these sort of advanced features are special to hearing aids, and are not found in personal hearing amplifiers.
More advanced digital hearing aids can connect to smart devices.Top-of-the-line noise processing and frequency action
All hearing aids procedure sound, which indicates that when sound gets here into the hearing aid, it needs to be sectioned into bands of sound (sometimes described as "channels") and digitized prior to it can be amplified. The better the listening devices, the more versatility it has to band noises that are amplified for your distinct hearing loss prescription.
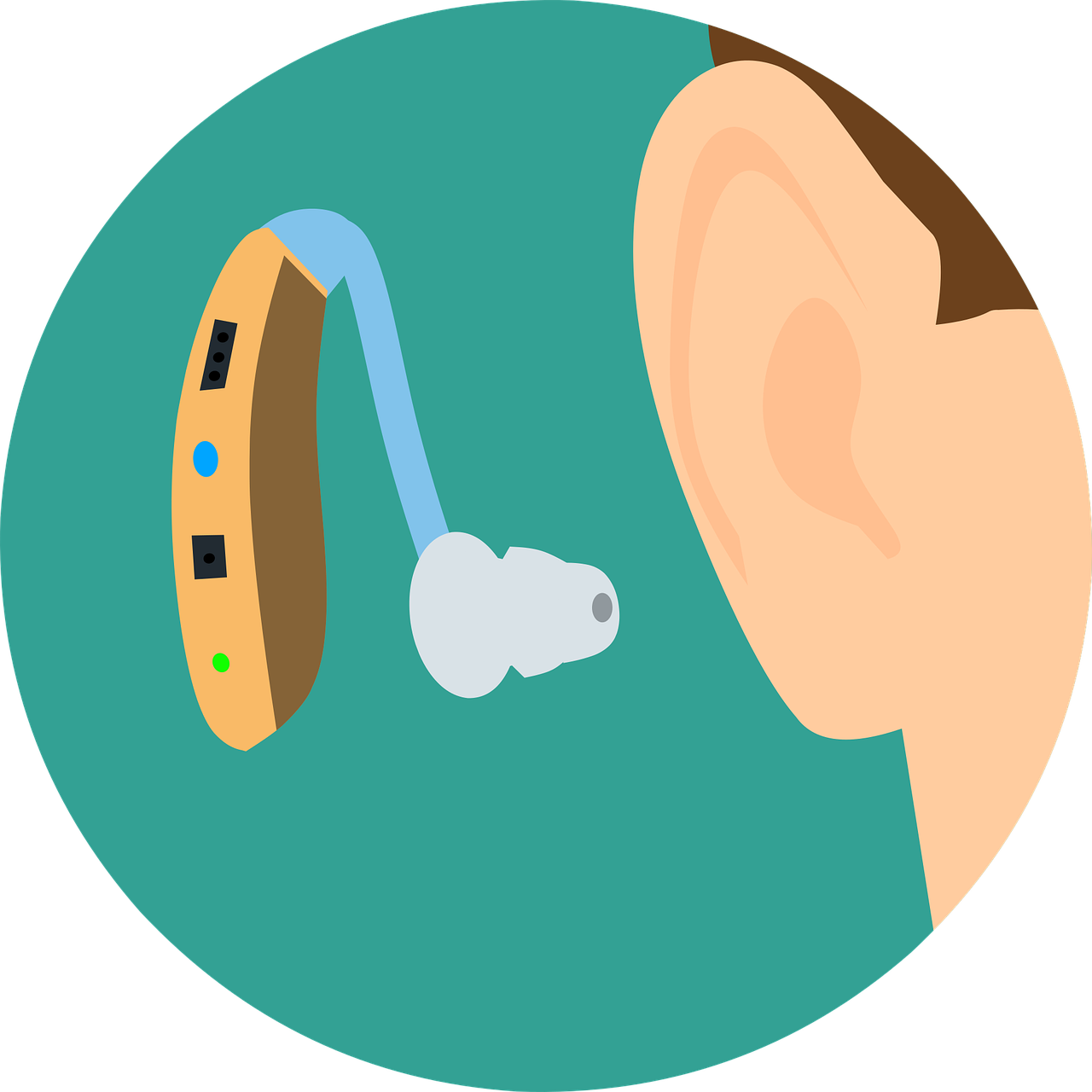
For example, if you have only high-frequency hearing loss, a better-made listening devices can amplify only those noises within that band, whereas a lower-end model may enhance mid- and high-frequency sounds. This personalization of the listening devices is called its frequency reaction.
Bluetooth compatibility
Bluetooth compatibility is a cordless feature that allows hearing aids to connect to mobile phones and other gadgets that utilize Bluetooth, often through an intermediary device. Bluetooth innovation has the ability to enhance the signal-to-noise ratio and get rid of feedback from the microphone due to the fact that the signal bypasses the microphone and directly goes into the listening devices's processor. A Bluetooth connection is also less most likely to experience interference, which can occur with an FM system (see listed below under standard features).
Artificial intelligence
Some premium hearing aids include artificial intelligence (AI), which enables them to access a deep neural network to process sound.

By logging volume control settings and program choices for certain sound environments, the hearing aids can begin to make these modifications instantly when the environment is identified. Essentially, a DNN permits hearing aids to begin to imitate how your brain would hear sound if your hearing wasn't impaired.
Apps
The homescreen for the Oticon On app for Oticon brand hearing aids.The majority of these days's innovative hearing aids come with smart device apps, permitting the user to make changes, contact their hearing care supplier, and display battery life. Most importantly, some of them work like assistive listening gadgets, by routing call or other sources of noises directly to a user's hearing aids. Some likewise can transform speech into text, and equate various languages.
Rechargeable batteries
Progressively, hearing aids have rechargeable batteries, allowing a person to stop switching out tiny button batteries every couple of days or weeks. It's prepared for that these will be commonly readily available with many listening devices models in the next couple of years.

Tinnitus masking features
The most sophisticated hearing aids come with ringing in the ears masking functions. An audiologist or other hearing care service provider can configure them to emit noises that mask the ringing in the ears or ringing in your ears. (But for lots of people with ringing in the ears, merely magnifying the sounds you've been missing out on with a listening devices can assist decrease tinnitus, which often develops when a person experiences age-related hearing loss.)
Standard listening devices innovation
Although programmable by computer system, standard hearing aids usually have limited adjustments offered for fine-tuning to fit unusual patterns of hearing loss. They are also less adjustable and automated than hearing aids with advanced technology.
Basic digital hearing aids also generally need you to make some manual changes in certain listening situations-- such as turning a volume control up or down, or pushing a button on the aids to minimize noise coming from behind.
The following are examples of functions that are typically consisted of in fundamental hearing aid innovation.
Wireless hearing aids
Wireless technology permits 2 hearing aids to run together as one complete system, instead of acting as 2 independent devices. The sound input to both hearing aids is shared and decisions about the digital noise processing are based on the integrated info. This is known as binaural processing. This innovation simulates the brain's ability to procedure details originating from both ears and helps reduce manual changes.
For example, if one listening devices is being triggered for directional mode, both hearing aids would likely change into that mode at the same time. The information transfer rates for wireless hearing aids are measured in nanoseconds, which is much faster than human brain can identify. For the user, the changes are perceived in real time. Noise processing is therefore synchronized between the two hearing aids, thus enhancing sound quality for the user.

Wireless hearing aids are also efficient in wirelessly interacting with external devices, usually via Bluetooth, telecoils that work with hearing loops, and frequency modulation systems, (the latter two we go over listed below).
In essence, cordless technology improves hearing aids in 2 ways:
By enhancing how hearing aids connect with each other (contemporary hearing aids can now provide noise as a collaborative set, rather of individually). By making it easier to get in touch with the world around you, along with your favorite devices, like mobile phones.Telecoil
A telecoil or tcoil is a wireless feature that gets electromagnetic signals from suitable telephones or looped spaces. This innovation has been available in hearing aids for a very long time. Due to the fact that the signal of interest is directed to the listening devices's processor without utilizing the microphone, telecoil can improve the signal-to-noise ratio while removing the capacity for feedback.

Public performances, trips, exhibits and praise services are commonly made accessible to individuals with hearing loss by means of telecoil.
FM compatibility
Frequency modulation (FM) compatibility is a wireless feature that enables hearing aids to get in touch with FM systems, in some cases via a special accessory to the hearing aids called a boot. FM systems can be used alone or with hearing aids. Like telecoil, FM systems improve the signal to sound ratio without triggering a feedback loop in the hearing aids. FM compatibility is particularly essential when selecting hearing aids for kids due to the fact that these systems are commonly used in instructional settings to ensure that the teacher's voice is heard above the shout of the classroom.
Directional microphone systems
Directional microphone systems are created to increase sounds originating from the front of the user and minimize sounds originating from other directions.

Various system designs shut out more or less of the sounds coming from behind the user. These systems improve speech understanding in background sound. Complete satisfaction is higher for hearing aids with directional microphone systems than for hearing aids without them.
Digital sound reduction
Digital noise decrease systems examine the signal to figure out if it includes unwanted sound. If this undesirable noise is detected, this system lowers the level of sound. This function makes the background or environmental noise less bothersome and increases your listening convenience. Digital noise decrease has been revealed to be reliable and chosen by hearing aid wearers.
Impulse noise decrease
Similar in function to the digital sound decrease, impulse noise reduction improves listening comfort. This system finds any transient loud noises, such as vehicle keys rattling, typing on a keyboard or meals rattling, and softens them quickly.
Wind sound decrease
Although relatively specific in its application, wind sound reduction can make a world of difference for those who hang around delighting in outdoor hobbies, like golf enthusiasts and boaters.

Wind noise decrease finds the impact of the wind blowing throughout the listening devices microphones and avoids or lowers the amplification of it.
Feedback management systems
Feedback management systems combat the inescapable feedback (whistling) that takes place in a hearing aid. These feedback loops produce a frustrating whistling sound that can obstruct of your convenience. Feedback management algorithms can be carried out in a different way for standard hearing aids or sophisticated hearing aids. Standard feedback management systems may decrease the general amplification to eliminate the whistling. Advanced feedback management systems minimize or eliminate whistling without impacting total amplification of the listening devices.
New hearing aid innovation includes. smart device compatibility. .Information logging
Data logging is a feature that shops data about the listening environments in which you wear your hearing aids and your preferences for programs, volume levels and other functions. The details can be accessed by the hearing healthcare professional when you return for a follow-up visit.

Your practitioner might use this important information to further tailor your listening devices fitting.
What are the real-world benefits of these features?
Picture being in a typical busy dining establishment, having dinner with friends. Sounds are originating from all directions, such as meals clanking, people talking and laughing at other tables and waiters hurrying about. You're using your new hearing aids and listening to a pal who is sitting across from you at the table. She's informing a joke. Your hearing aids are simultaneously minimizing impulse sounds like silverware clanking onto a plate (impulse noise decrease), minimizing the whir of the ventilation system above (digital sound decrease), suppressing the voices of the people at the tables behind you (directional microphone system) and keeping info about the listening environment to be saved for later fine-tuning (data logging). They're doing all of this automatically while magnifying and shaping the speech signal from your good friend.
You are free to unwind and enjoy the laugh line.
This is just one example of today's advanced hearing aid technology in action. Contact a hearing professional in your location to discover hearing aids near you.
Find a center.We have more hearing clinic evaluations than any other website!
Related content. Why do we have two ears? What are hearing aid settings? And how do I tailor mine? How to use earphones with hearing aids. Hearing aids with artificial intelligence. Hearing aid apps: What you require to understand. For how long do hearing aids last? The Healthy Hearing Report. post. Can allergic reactions cause hearing loss? short article. How to inform your parents they need hearing aids. faq. What you need to learn about earwax. post. Four typical causes of short-term hearing loss in children.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment